A mobile operating system is an operating system for smartphones, tablets, smart watches/bands and other mobile devices. This is not to be confused with laptops which are mobile (can be carried about), but use a different computing platform. A mobile operating system is known as a mobile OS for short.
Older mobile OS are purely embedded systems that are focused on telecommunication (calls and SMS). Modern mobile OS are programmed and designed to make smartphones run like mini PCs. They combine PC features such as gaming or photo/video editing, with the older traditional telecommunication function for calls and SMS. This has made the mobile platform to be more versatile than desktop/PCs. However, not withstanding these facts, PCs remain ahead in terms of sheer processing power.
On a smartphone, the mobile OS is divided into two: the front end which faces the user and handles tasks; and the back end which handles the hardware as well as radios and network connectivity.
Read: What is system software?
The evolution of the Mobile Operating System
As mobile phones have evolved through the years, so have the software that has been made for them.
The 90’s
Pre 1993, all mobiles used proprietary embedded systems. In the year 1993, that would change as hardware had matured to a point where software could be installed, rather than embedded on them.
One of the first OS to be made is the Penpoint OS, developed by GO corporation. Later that same year, Apple launched the Newton OS. The next year (1994), Magic OS was introduced. In 1996, Palm OS also joined the growing list of new operating systems.
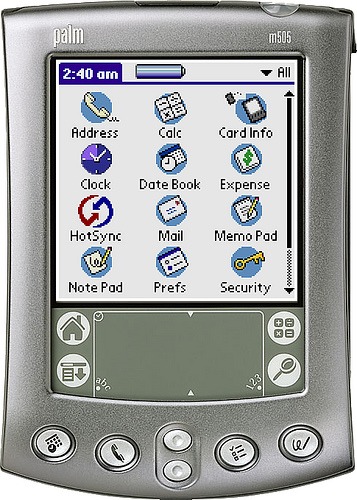
Early operating systems were written mostly in C++, a high level programming language. A common theme with these operating systems is that they were closed sourced, proprietary and could not communicate with one another. This would soon change.
In 1998, Psion, Ericsson, Nokia and Motorola will come together to form the Symbian limited and jointly develop the Symbian OS. Nokia, as it turns out, will benefit the most out of this arrangement.
Despite the formation of the Symbian Ltd. Nokia would go on to launch the Nokia N7110 with its own proprietary OS, the S40 platform. It was far ahead of most mobile OS of the time, having features such as T9 predictive text and a WAP browser. These were features which other OS did not support at the time.

The 2000s
In 2001, Nokia officially released the first Symbian OS phone, the Nokia 9210 communicator. It was one of the best “smartphones” of its time. This Symbian OS version is the first OS that allowed users to download and install additional software on their phones.
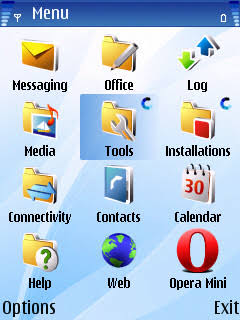
Nokia would then take features from their S40 platform and add them to the Symbian OS. From this point onward, Symbian would become the dominant OS, not only on Nokia phones, but on the entire market as Samsung and Sony Ericsson would also adopt it.

One notable OS in this period is the Java 2 Micro edition (J2ME) by Sun Microsystems which were later bought by Oracle. The J2ME in the true sense of the word is not an Operating System. It is a software platform that allowed software developers to code apps and games for mobile devices. The J2ME platform ran on other OS such as the aforementioned Symbian OS. Phone that supported J2ME and could install games from WAP sites like Sefan were commonly called Java phones.
Read: Front end and back end software
Other OS in the time period between the year 2000 and 2006 include Windows CE (Microsoft), Linux, Montavista and Maemo OS (Nokia).
The game changes
In January 2007, Steve Jobs of Apple inc. announces the iPhone OS which would later be renamed to iOS. The new iPhone OS completely eclipsed the Symbian OS with its support for full internet access instead of WAP as well as an App Store.
The next month, Microsoft released Windows Mobile 6.0. Palm also announced the Palm foleo in May but cancelled it in September of the same year.
In June, the first iPhones were released and sold to the public. It was a huge seller that sold 1 million phones about 2 months after its release.
The success of Apple’s iPhone made the giants of the industry sit up. Most of them had written Apple and its iPhone off as a failure and they were genuinely stunned. Apple’s competitors needed to respond and the answer came in the form of a little known software known as Android.
In November 2007, the Open Handset Alliance (OHA) was established with about 34 members. The main ones were Google, HTC, Sony, Dell, Samsung, LG and Motorola. Notable absentees are Nokia and BlackBerry. The OHA adopted Google’s Android as its OS.
In 2008, another group known as LiMo (Linux Mobile) was formed by Motorola, NEC, NTT DoCoMo, Panasonic, Samsung and Vodafone. LiMo is now known as Tizen OS. In June of the same year, Nokia becomes the sole owner of Symbian and wanted to build its own group. Something similar to the OHA (Android) or the LiMo (Tizen). In October, the first Android phone known as the HTC Dream was released.
2009 – 2019
Between 2009 to 2019, a host of new mobile OS would be released and would also die off. This first to go was the Palm OS (2009) which was replaced with Web OS. The Nokia N900 was the only device to run Maemo OS which was subsequently killed off.
In 2010, Samsung introduced Bada OS and HP bought Web OS. Microsoft killed off previous iterations of its mobile OS and introduced Windows Phone OS. In 2011, Nokia abandoned Symbian and switches to Windows. Mozilla develops and releases Firefox OS. HP kills off Web OS and Nokia abandons MeeGo.
In 2012, a group of former Nokia employees formed Jolla. Jolla picks up MeeGo and renames it Sailfish OS. Samsung kills off Bada OS. In 2013, LG would buy Web OS from HP. The next year, Microsoft launched Windows 8.1 and Samsung releases the first phone with Tizen OS.
In 2015, BlackBerry kills off BlackBerry OS and in 2019, Windows Mobile was discontinued.
The Present
As it stands, the mobile operating system landscape is dominated by Android and iOS. Android has the lion’s share of the market as most of the OS and UIs around are Android based.
The other OS include Harmony OS, Fire OS (Amazon), Chrome OS (Google), Sailfish OS, Tizen, Kai OS (Kai), Lite OS (Huawei), Fuchsia, Pure OS, Ubuntu touch, Plasma OS etc.
Thank you for reading to the end. As always, ensure to check out our links for more information and…
- Subscribe to my YouTube channel
- Follow on Facebook
- Join our Telegram community
- Participate on Reddit
- Find us on Quora
